[Mobility Inside] Unlocking the Future of Mobility With DX

With digital transformation (DX) powered by the cloud, Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI) and big data now on the minds of many, more and more businesses have been going through ‘digitalization’ to stay ahead of the game – or not be left behind. For automotive companies, this could not be more vital to their evolution.
The cars of tomorrow will be controlled by high-performance computing, system on chips and software platforms, which means carmakers will have to start spending more time and money on analysis, design, development, verification and maintenance. To carry out these processes in the most efficient way, firms require a powerful strategy that goes beyond the capabilities of analog methods. This is where DX comes in to change the way we handle data.
Let’s examine a few of the countless ways DX is ready to shape future mobility.
DX of Automotive Parts Development Process
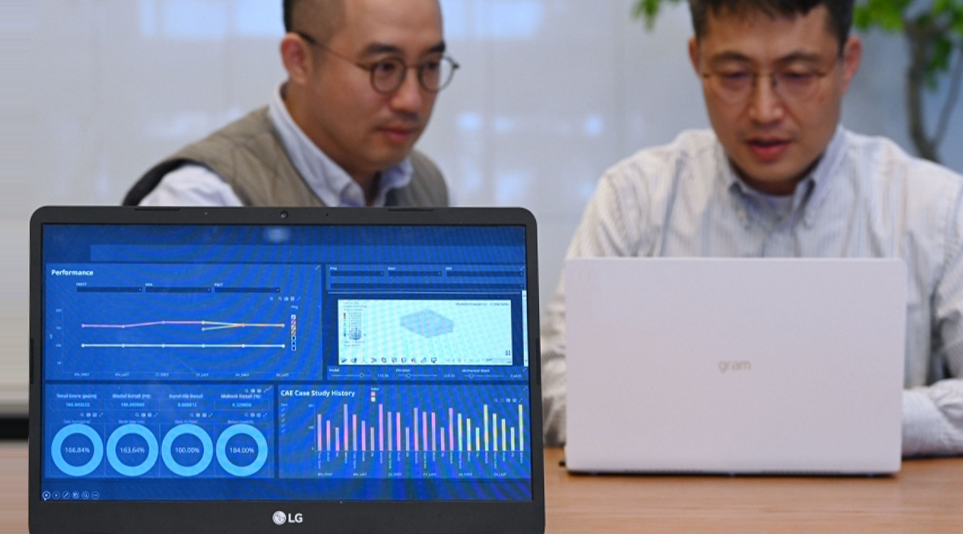

As a major provider of vehicle components, LG is integrating DX into its development process in an effort to improve product quality and accelerate growth. From last year, LG’s researchers even started planning an AI validation platform developed with Altair, a U.S. company that has specialized in information technology based on software and cloud solutions for simulation, computing and AI technologies since 1985. This platform standardizes data measured at certain times and uses AI technology to clearly visualizes results.
Through this platform, LG can develop enhanced reliable automotive parts by predicting the performance of every stage of development. In addition, the platform can automate performance validation and systematically manage the vast amount of simulation data generated during the development process to speed up development. For example, if a customer requests a new requirement, engineers can access the AI platform to virtually predict performance and give several options for them to choose from.
Data accumulated during verification are continuously learned to hone prediction accuracy. This data can then be applied to various processes from planning and mass production to the improvement of each product’s quality and performance.
DX of Global Premium Automakers

So, how are global automakers applying DX in development? A leading North American electric vehicle (EV) company has been applying over-the-air (OTA) to all its vehicles since 2014, which has allowed it to gradually accumulate data from the road and on the performance of components and batteries.
All of this is possible thanks to a vast amount of collected data that gives carmakers the ability to quickly and accurately learn how to change battery combinations, integrate parts and remove unnecessary specifications. As vehicles can be developed more efficiently and necessary resources can be continuously reduced, the use of vehicle data has become essential across the sector.
DX More Important for Contactless Car Management Services

DX isn’t limited to the early stages of development. With the expansion of contact-free services in sales, management and after-sales service, another aspect of DX is emerging. A prime example of this is the ability to compare care quotes, reserve maintenance and make payments all at once via a smartphone app. Comparing price, quality and options as well as searching for reviews are also being done online, so consumers only need to look online when deciding which car to buy. With the rise in contact-free services since the pandemic changed the world in 2020, digitalization is expected to accelerate across industries.

Automakers and suppliers are leveraging DX to achieve greater efficiency and reduce costs. As more people use cars and more data becomes available, digitalization has the potential to increase the size of the pie for various stakeholders, including car manufacturers and service providers.
With DX paving the way forward in the automotive space, make sure to watch this space and be the first to discover the immense features and power of the cars on the horizon.
# # #





![[Mobility Inside] Protecting Your Data, Keeping You Safe: Why Cybersecurity Matters](https://www.lgnewsroom.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Cyber-Security-fi-e1682489736850-403x272.png)
![[Mobility Inside] Exploring the Minds of Drivers Like Never Before](https://www.lgnewsroom.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/IoB_fi-e1678682409500-403x272.png)
![[Mobility Inside] The Secret to Tailored Driving Experiences: Camera Sensors](https://www.lgnewsroom.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Camera-Sensors-fi-e1682491277592-403x272.png)


